
Evolution is a part of life, whether of humans or animals. Some creatures evolve in the usual way, whereas others adapt in bizarre ways and with unusual traits. From surprising facts to strange and frightening changes, here are 10 unusual traits of animal evolution.
Bioluminescence
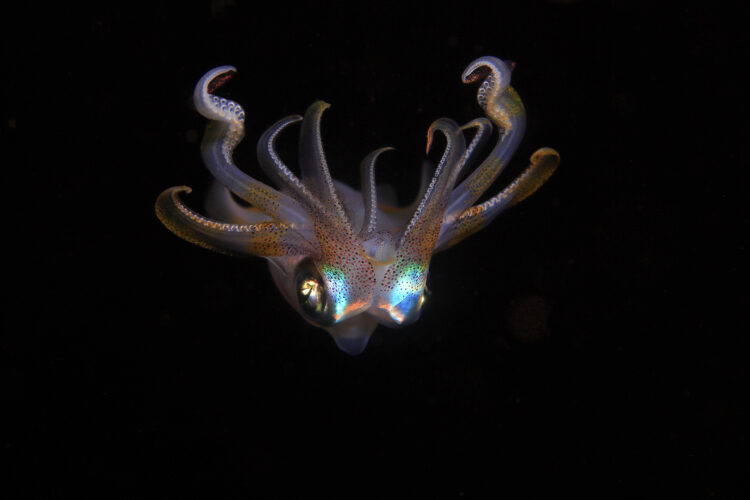
Bioluminescence is a surprising trait of animal evolution. It defines the capacity of some organisms to emit light through biological reactions. This amazing adaptation can be seen in fireflies, certain fungi, and some deep-sea animals. Bioluminescence serves a variety of functions, like communicating, luring prey, and deterring predators.
Echolocation

Echolocation is a sensory process, an unusual trait amongst creatures like dolphins and bats. This process allows them to find objects by sending out sound waves and listening for the returning echoes. These animals have an amazing adaptation that allows them to see their environment in completely dark or murky water.
Electric Organs

There are nearly 200 fish species, including the electric eel, electric rays, eels, electric catfish, and others, with bioelectric organs. These fishes have specialized organs that can produce electric fields. These organs serve as defense, navigation, and communication tools for them. Amongst many animal evolutions, the capacity to generate electricity has independently developed in parallel to other evolutionary factors.
Mimicry
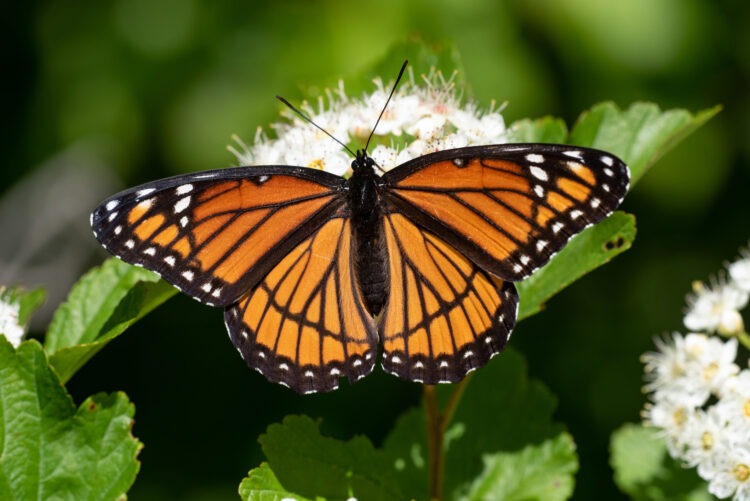

No, we humans are not the only ones to copy or mimic others; some animals do that as well. Within animal evolution, mimicry is the process where species evolve to begin resembling one another. They do so either to evade predators or obtain access to resources. Some harmless snakes imitate the coloring of venomous species to ward off predators. Similarly, viceroy butterflies replicate the coloration of monarch butterflies to evade predation.
Detachable Body Parts

Animal evolution has brought characteristically changes in animals. Another unusual trait that surprises us is the ability to freely separate bodily parts. It helps animals reproduce or serve as a defense mechanism. Some species of sea cucumbers can detach from their internal organs. Similarly, certain lizards can detach their tails to escape.
Extreme Size Reduction

Throughout different stages of animal evolution, some animals evolved to be incredibly small. This has happened majorly due to the adaptation of animals to a particular ecological environment. It occurred where being small has benefits like improved agility, easier access to small prey, or lower resource requirements.
Regeneration
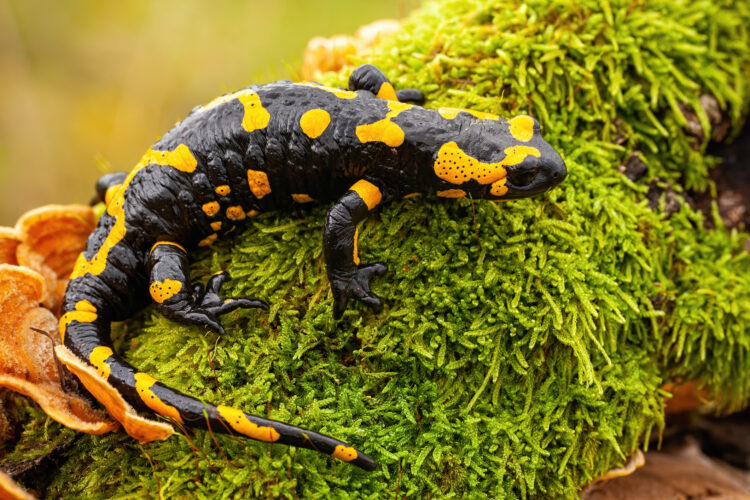

Do you know some animals can regenerate? Yes, certain animals can grow back missing body parts (organs or limbs). This evolutionary trait allows them to fight off predators and heal wounds more quickly. This evolution enables them to increase their chances of surviving and procreating. Animals like salamanders, lizards, geckos, and iguanas are known for their regenerative abilities.
Parthenogenesis

Parthenogenesis is a form of reproduction that allows females to bear children without the need for male fertilization. Certain species of fish, reptiles, and insects have this unusual characteristic that allows them to reproduce quickly in favorable environments or when they do not have suitable partners.
Social Parasitism

Social parasitism is an evolutionary feature when one species takes advantage of the social structure/behavior of another species to further their interests. This can take many different forms, from sneaking into other creatures’ nests or colonies to laying eggs, tricking hosts into taking care of their young, or stealing host individuals or groups of their resources.
Photosymbiosis (In Body Parts)
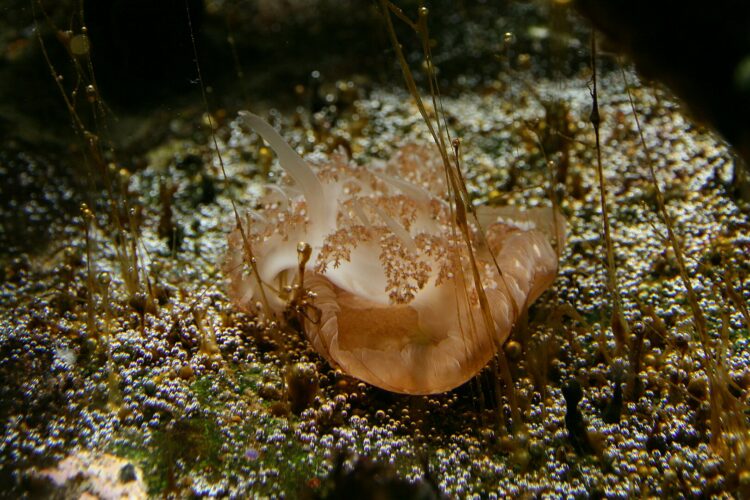

Certain animals developed symbiotic relationships with bacteria, algae, or other photosynthetic organisms, which allow them to use sunlight as a source of energy. This process, called photosymbiosis or kleptoplasty, is seen in some marine animals, such as sea slugs. They absorb chloroplasts from algae and merge them into their tissues to enable a limited degree of photosynthesis.

Comments
Loading…