12 Health Tests Women Over 50 Shouldn’t Skip

Reaching your fifties brings wisdom, confidence, and new adventures. However, your body also starts changing in ways that require closer attention to your health. Regular checkups and specific screenings become more important than ever during this stage of life. Making smart choices about preventive care now can help you stay healthy and catch potential problems early when they’re most treatable.
1. Mammogram Screening
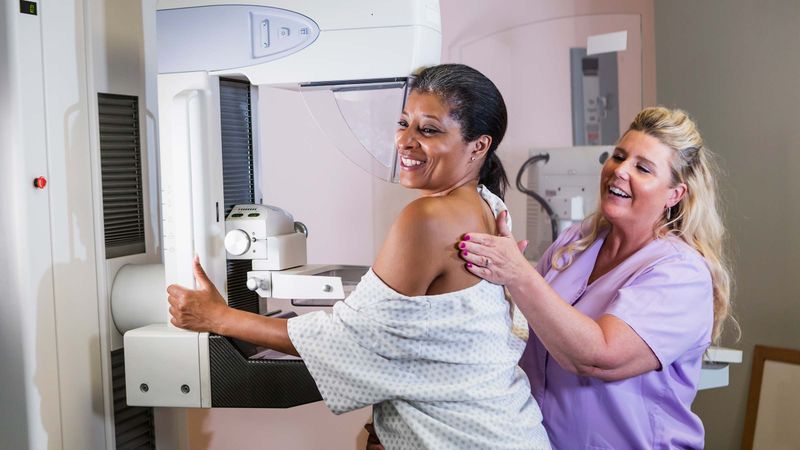
Breast cancer risk increases significantly after age 50, making annual mammograms one of your most important health appointments. Early detection through mammography can catch tumors before you can feel them, dramatically improving treatment outcomes.
Most doctors recommend yearly mammograms starting at age 50, though some suggest beginning at 40. The procedure takes about 20 minutes and involves compressing breast tissue between two plates for X-ray images.
Schedule your mammogram for the week after your period when breasts are least tender. Don’t wear deodorant or lotion on the day of your appointment, as these can interfere with the imaging results.
2. Bone Density Test
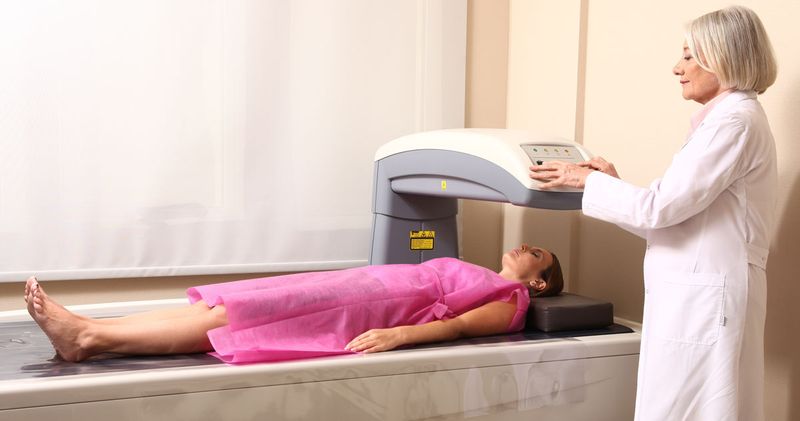
Osteoporosis silently weakens bones, especially after menopause when estrogen levels drop. A bone density test, called a DEXA scan, measures how strong your bones are and whether you’re at risk for fractures.
This painless test takes about 15 minutes and uses low-dose X-rays to scan your spine and hips. The results show if you have normal bone density, osteopenia (mild bone loss), or osteoporosis (severe bone loss).
Getting baseline measurements in your fifties helps your doctor track changes over time. If problems are found early, treatments like calcium supplements, vitamin D, and weight-bearing exercises can help strengthen your bones significantly.
3. Colonoscopy Examination
Colorectal cancer becomes more common after age 50, but it’s also highly preventable with regular screening. Colonoscopy remains the gold standard for detecting polyps before they become cancerous.
During this procedure, a doctor uses a flexible tube with a camera to examine your entire colon. Most polyps can be removed immediately during the same visit, preventing future cancer development.
While the preparation involves drinking a special solution to clear your bowels, the actual procedure is done under sedation so you won’t feel discomfort. If results are normal, you typically won’t need another colonoscopy for ten years, making this inconvenience worthwhile for long-term peace of mind.
4. Cardiovascular Risk Assessment

Heart disease kills more women than any other condition, yet many don’t realize their risk increases dramatically after menopause. Comprehensive cardiovascular screening goes beyond basic blood pressure checks to evaluate your overall heart health.
Testing typically includes cholesterol panels, blood sugar levels, and sometimes an electrocardiogram or stress test. Your doctor may also measure inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein that indicate hidden heart disease risk.
Family history, smoking, diabetes, and high blood pressure all increase your cardiovascular risk. Understanding your numbers helps you make lifestyle changes or start medications that can prevent heart attacks and strokes before they happen.
5. Cervical Cancer Screening
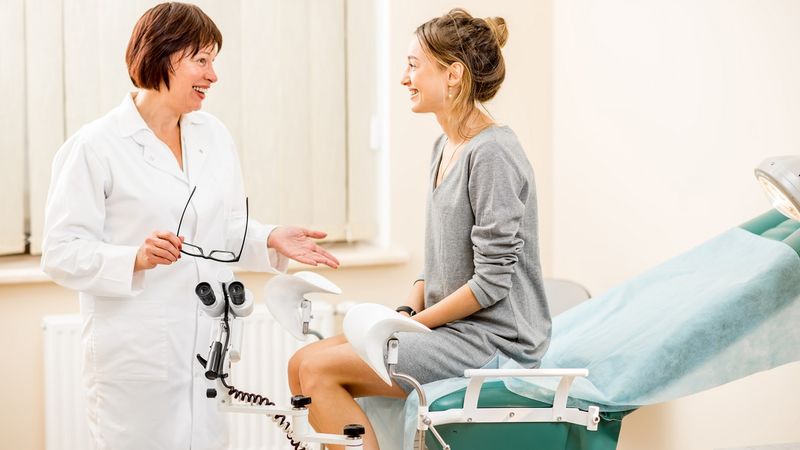

Many women mistakenly believe they can stop getting Pap smears after menopause, but cervical cancer screening remains important through your sixties. HPV infections can persist for decades before causing problems.
Current guidelines recommend Pap smears every three years or HPV testing every five years for women over 50. Your doctor may suggest stopping screenings at age 65 if you’ve had consistently normal results.
The test takes just a few minutes during a routine pelvic exam. While cervical cancer rates decrease with age, catching precancerous changes early allows for simple treatments that prevent cancer from developing. Don’t skip this important screening just because you’re past childbearing years.
6. Eye Examination and Glaucoma Test
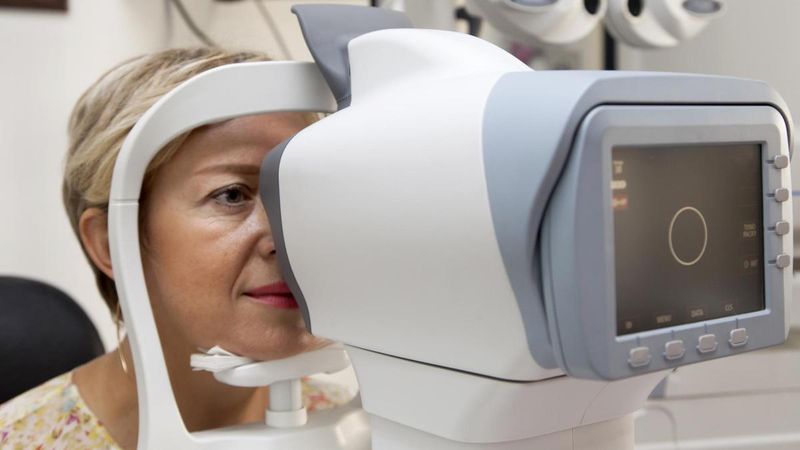
Vision changes accelerate after 50, and serious eye diseases like glaucoma often develop without symptoms. Comprehensive eye exams can detect problems before they affect your sight permanently.
Glaucoma testing measures pressure inside your eyes and examines your optic nerve for damage. Macular degeneration screening looks for changes in your central vision that could indicate age-related eye disease.
Annual eye exams also check for cataracts, diabetic retinopathy, and other conditions that become more common with age. Early detection allows for treatments that can preserve your vision and maintain your independence. Don’t wait until you notice vision problems to schedule your appointment.
7. Thyroid Function Test
Thyroid problems affect women five times more often than men, especially after menopause. Symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, and mood swings are often dismissed as normal aging when they could indicate thyroid disease.
A simple blood test measuring TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) can detect both overactive and underactive thyroid conditions. Additional tests may check T3 and T4 hormone levels for a complete picture.
Untreated thyroid problems can affect your heart, bones, and mental health. The good news is that most thyroid conditions respond well to medication, often dramatically improving energy levels and overall wellbeing within weeks of starting treatment.
8. Skin Cancer Screening
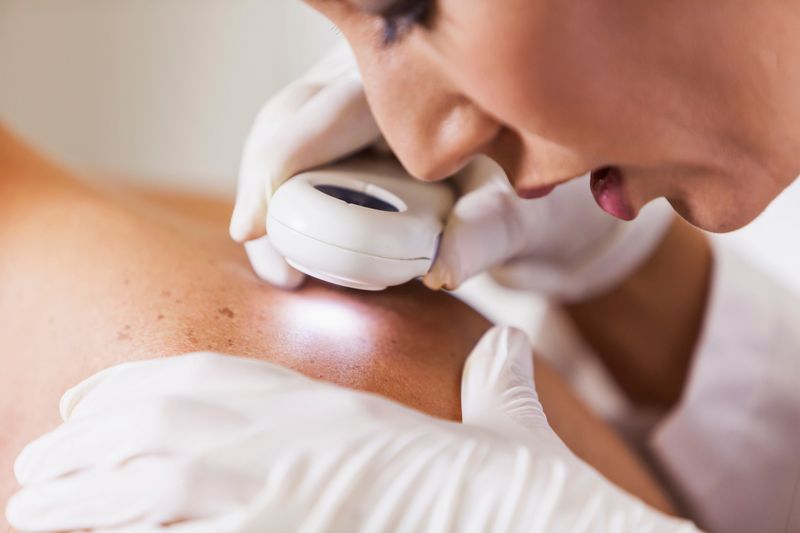
Decades of sun exposure catch up with you in your fifties, making skin cancer screening essential. Melanoma rates increase with age, but early detection leads to excellent survival rates.
A dermatologist examines your entire body, looking for suspicious moles, spots, or growths. They use special tools to see details invisible to the naked eye and may photograph concerning areas to track changes.
Schedule annual full-body skin checks and perform monthly self-examinations at home. Look for moles that change color, size, or shape, and don’t ignore new growths. Many skin cancers are completely curable when caught early, making this screening both simple and potentially life-saving.
9. Diabetes and Blood Sugar Testing
Type 2 diabetes risk increases significantly after age 50, especially if you’re overweight or have a family history. Unfortunately, early diabetes often has no symptoms, allowing blood sugar damage to occur silently.
Screening involves fasting blood glucose tests or hemoglobin A1C measurements that show your average blood sugar over three months. Prediabetes can also be detected, allowing for early intervention.
Catching diabetes early prevents serious complications like heart disease, kidney damage, and vision problems. Lifestyle changes including diet modifications and regular exercise can sometimes prevent or reverse prediabetes, making early detection incredibly valuable for your long-term health.
10. Blood Pressure Monitoring
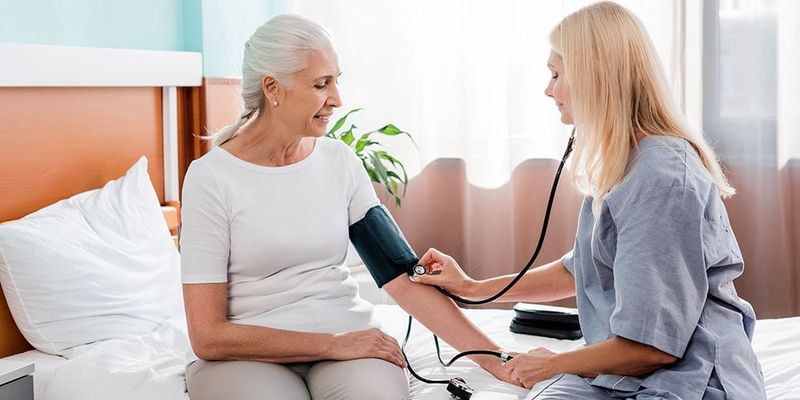

High blood pressure becomes increasingly common after menopause, earning its nickname as the silent killer because it rarely causes symptoms. Regular monitoring helps catch hypertension before it damages your heart, kidneys, or brain.
Blood pressure should be checked at every doctor visit, but home monitoring provides better information about daily fluctuations. Normal readings are below 120/80, while anything over 140/90 indicates high blood pressure.
Lifestyle changes like reducing salt intake, exercising regularly, and managing stress can lower blood pressure naturally. When needed, medications are highly effective at preventing strokes and heart attacks caused by uncontrolled hypertension.
11. Hearing Assessment
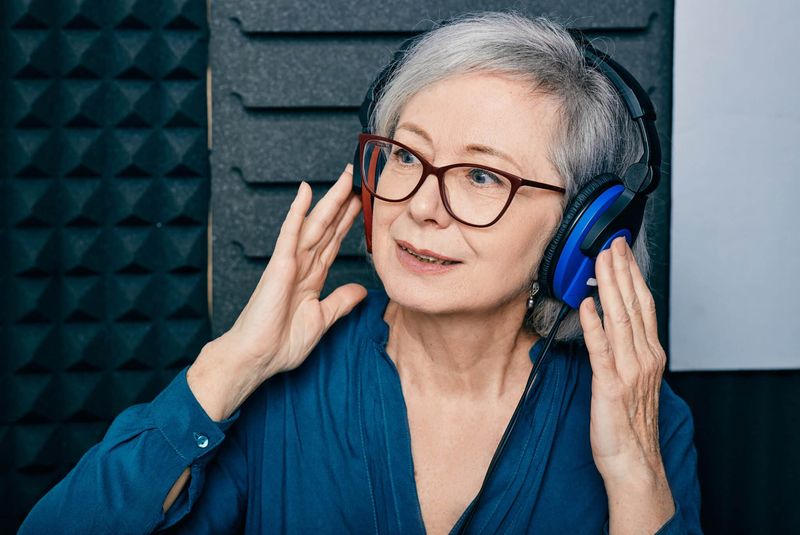

Age-related hearing loss affects one in three people over 50, yet many wait years before seeking help. Untreated hearing loss can lead to social isolation, depression, and even cognitive decline.
Audiologists use various tests to measure your ability to hear different frequencies and understand speech in noisy environments. Baseline hearing tests help track changes over time and determine when intervention is needed.
Modern hearing aids are smaller, more effective, and less noticeable than ever before. Early treatment helps maintain your quality of life and keeps you connected to family and friends. Don’t let pride prevent you from addressing hearing changes that could be easily corrected.
12. Mental Health Evaluation
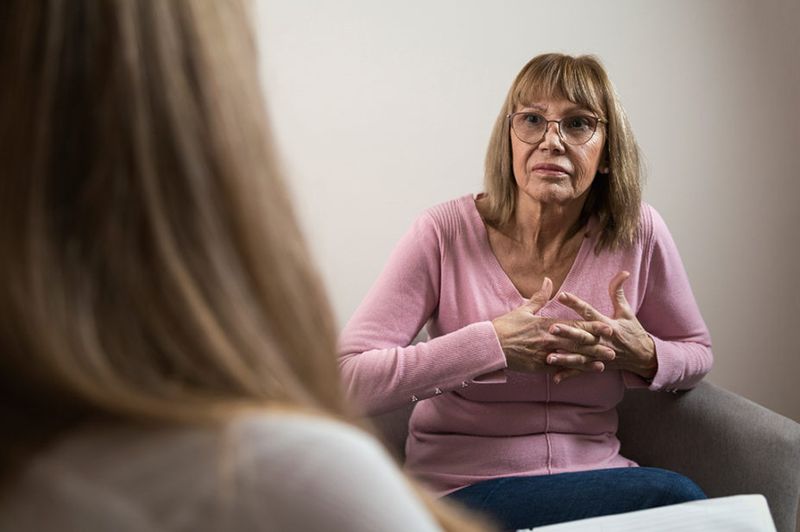

Depression and anxiety often emerge or worsen during menopause and beyond, yet mental health concerns are frequently overlooked in older women. Hormonal changes, life transitions, and health issues can all impact emotional wellbeing.
Mental health screenings involve questionnaires and discussions about mood, sleep, energy levels, and life satisfaction. Primary care doctors can perform basic assessments, while specialists provide more comprehensive evaluations.
Treatment options include therapy, medication, or lifestyle changes depending on your specific needs. Addressing mental health concerns improves not only your emotional state but also your physical health, relationships, and overall quality of life during this important life stage.

Comments
Loading…