These 13 Myths Refuse to Die — Even Today

Some stories sound so believable that people keep sharing them without checking the facts.
From health advice to old superstitions, certain myths have stuck around for decades or even centuries.
Science has proven many of these wrong, but they still pop up in conversations and on social media.
1. Cold Weather Gives You a Cold

Your mom probably told you to bundle up or you’d catch a cold, but temperature alone doesn’t make you sick.
Viruses cause the common cold, not chilly air or wet hair.
People get sick more often in winter because they spend more time indoors where viruses spread easily.
Close contact with infected people in heated, crowded spaces helps germs jump from person to person.
Going outside without a jacket might make you uncomfortable, but it won’t give you the sniffles.
Washing your hands regularly and avoiding sick people are far better ways to stay healthy than wearing extra layers.
2. Humans Only Use 10% of Their Brains
Movies love this myth because it makes for exciting stories about unlocking hidden powers.
Brain scans show we actually use all parts of our brain throughout the day, just not all at once.
Different brain regions handle different tasks like breathing, moving, thinking, and feeling.
Even simple activities light up multiple brain areas working together.
Brain damage to even small areas can cause serious problems, proving every part matters.
Scientists have never found a “silent” section of brain tissue that serves no purpose.
Evolution wouldn’t give us extra brain tissue we don’t need since brains use lots of energy.
3. Lightning Never Strikes the Same Place Twice

Tell that to the Empire State Building, which gets hit about 25 times every year!
Lightning actually prefers to strike the same spots repeatedly, especially tall structures and high points.
This myth might comfort people during storms, but it’s completely backwards.
Places that got struck once are often more likely to get hit again because they have features that attract lightning.
If you’re outside during a storm and see lightning hit nearby, that exact spot remains dangerous.
Stay away from tall trees, metal objects, and open fields where lightning commonly strikes multiple times.
4. Sugar Makes Kids Hyperactive

Parents swear birthday cake turns children into wild tornadoes, but controlled studies tell a different story.
When researchers give kids sugar without parents knowing, adults can’t tell which children ate sweets and which got sugar-free treats.
Exciting events like parties naturally make kids energetic and loud.
Parents expect sugar to cause hyperactivity, so they notice normal kid behavior more when sweets are around.
While sugar isn’t great for teeth or overall health, it doesn’t actually change behavior.
The myth persists because confirmation bias makes us remember times that match our beliefs and forget times that don’t.
5. Cracking Your Knuckles Causes Arthritis

That satisfying pop might annoy people around you, but it won’t damage your joints.
The sound comes from gas bubbles bursting in the fluid between your joints, not bones grinding together.
Studies comparing lifelong knuckle-crackers to non-crackers found no difference in arthritis rates.
One doctor even cracked the knuckles on one hand for 60 years while leaving the other hand alone, and both hands stayed equally healthy.
Arthritis develops from factors like age, genetics, injuries, and certain diseases.
If cracking bothers you for other reasons, feel free to stop, but don’t worry about your joint health.
6. Shaving Makes Hair Grow Back Thicker
Countless people avoid shaving because they fear creating coarser, darker hair.
Shaving only cuts hair at the surface and can’t change what happens at the root where growth actually occurs.
Hair feels stubbly when growing back because you’re touching the blunt edge created by the razor.
Unshaved hair has a natural tapered tip that feels softer, creating an illusion that shaving changed the hair itself.
Hair might look darker after shaving because short stubble hasn’t been lightened by sun exposure yet.
Your hair follicles have no way of knowing whether you shaved, so they keep producing exactly the same type of hair.
7. Goldfish Have Three-Second Memories

Goldfish get insulted by this myth constantly!
Research proves these little swimmers can remember things for months, not seconds.
Scientists have trained goldfish to push levers for food, recognize different shapes, and navigate mazes.
They remember feeding schedules and can even recognize their owners’ faces.
Goldfish also learn to avoid areas where they’ve been scared or hurt.
Their brains might be tiny, but they’re perfectly capable of forming lasting memories.
This myth probably started because goldfish seem surprised every time they circle their bowl, but they’re just exploring their environment like curious pets do.
8. Eating Before Swimming Causes Cramps

Generations of kids have waited impatiently on beach towels because of this rule.
While eating a huge meal before intense swimming isn’t ideal, a regular snack won’t cause dangerous cramps.
Your body can definitely digest food and swim at the same time.
Blood flow to your stomach increases during digestion, but not enough to starve your muscles of oxygen during normal swimming.
Real swimming cramps usually come from dehydration, cold water, or overworking tired muscles.
Professional swimmers often eat before training without problems.
Feel free to have a reasonable snack before jumping in the pool, just maybe skip the triple cheeseburger.
9. Bulls Get Angry at the Color Red

Matadors wave red capes in bullfights, but the color doesn’t matter at all.
Bulls are actually colorblind to red and see it as a shade of gray or brown.
What makes bulls charge is the movement of the cape, not its color.
Bullfighters could wave blue, green, or polka-dotted fabric and get the same reaction.
The red cape is a tradition that makes the spectacle more dramatic for human audiences.
Tests with different colored capes prove bulls respond equally to all moving objects.
So wearing red clothes around cattle won’t put you in extra danger compared to any other color.
10. Touching a Baby Bird Makes Its Mother Reject It
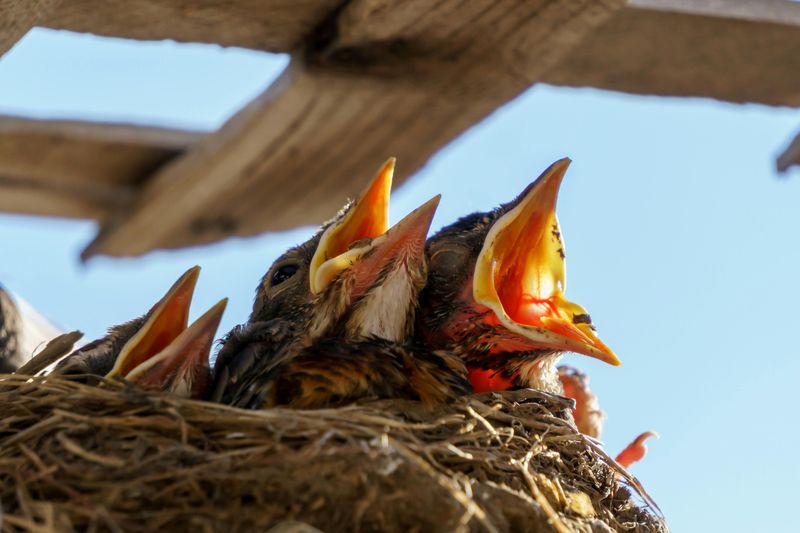

Well-meaning people leave baby birds in dangerous situations because of this myth.
Most birds actually have a poor sense of smell and won’t notice human scent on their babies.
Parent birds are devoted to their offspring and rarely abandon them for any reason.
They invest too much energy raising babies to give up just because something touched them.
If you find a baby bird, the best action depends on its age and situation.
Featherless babies should be gently returned to nearby nests, while fully feathered fledglings often belong on the ground learning to fly.
Their parents are probably watching from nearby branches.
11. You Lose Most Body Heat Through Your Head

Military studies from the 1950s tested soldiers in cold weather while wearing full winter gear except hats.
Obviously they lost heat from their only exposed body part, but this created lasting confusion.
Your head accounts for about 10% of your body’s surface area and loses roughly 10% of your heat.
There’s nothing special about your head compared to other body parts when it comes to heat loss.
Wearing a hat in winter is still smart because any exposed skin loses heat faster than covered skin.
But leaving your hands, feet, or legs uncovered would cause just as much heat loss as a bare head.
12. Bats Are Blind
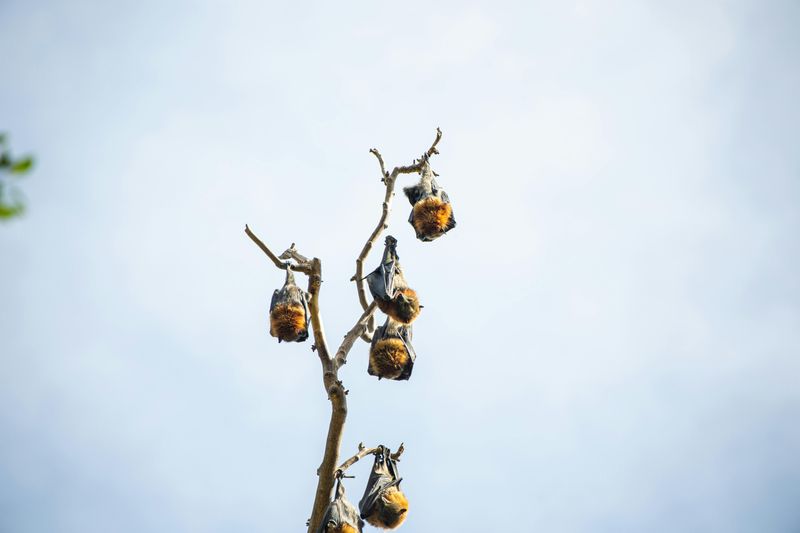

The phrase “blind as a bat” completely misrepresents these amazing flyers.
All bat species can see, and some actually have excellent vision, especially for detecting movement in low light.
Bats use echolocation to hunt in complete darkness, making high-pitched sounds and listening for echoes.
This incredible ability led people to wrongly assume bats lacked working eyes.
Different bat species rely on vision and echolocation in varying amounts.
Fruit bats have large eyes and depend heavily on sight to find food.
Even bats that prefer echolocation still use their eyes for navigation and recognizing landmarks during daylight.
13. The Great Wall of China Is Visible from Space
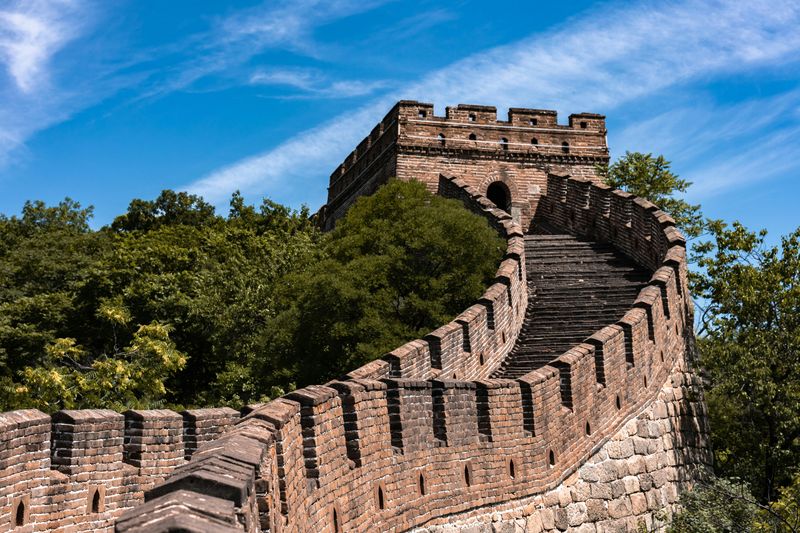

Astronauts have repeatedly debunked this popular claim.
From low Earth orbit, you can see cities, rivers, and coastlines, but the Great Wall is too narrow and blends with the surrounding landscape.
This myth likely started before space travel when people imagined what might be visible from such heights.
The wall is certainly long, stretching thousands of miles, but length doesn’t matter as much as width and contrast.
With powerful cameras and perfect conditions, astronauts might photograph the wall, but they can’t see it with their naked eyes.
Many highways are wider than the Great Wall, and nobody claims those are visible from space.

Comments
Loading…