
Aphasia is a disorder that can make even the simplest kinds of communication difficult. In this list, you will find ten key features of aphasia that may vary from its types and origins to everyday life. Our goal is to describe this term and inform others of the difficulties a person with this condition experiences.
Definition

Aphasia is a condition that hinders one’s ability to communicate and is the outcome of damage to the brain, leading to impairments in speaking, understanding, reading, and writing. Research indicates that the extent of aphasia ranges from mild cases when communication is notably diminished, to severe cases, when communication is almost completely eliminated.
Different Types

People with Broca’s aphasia comprehend spoken language but not speaking and writing. People with Wernicke aphasia speak in long, intricate sentences that do not make sense or include extra words. Individuals with global aphasia have serious difficulties, such as trouble understanding and the inability to communicate.
Causes of Aphasia
Other than heart stroke, causes of aphasia also include an injury to the brain that affects the language-processing section. Brain tumors that put stress on or harm these parts of the brain can also cause aphasia. Chronic forms of aphasia can develop due to infections such as encephalitis and several neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s, as well as some forms of dementia, as the brain slowly breaks down.
Symptoms of Aphasia

People with aphasia normally struggle to identify the appropriate terms for objects, recognized as anomi, and sometimes employ the incorrect terms or speak obliquely. In the worst cases, an individual may only be able to articulate a few phrases or repeat the same words or phrases again and again.
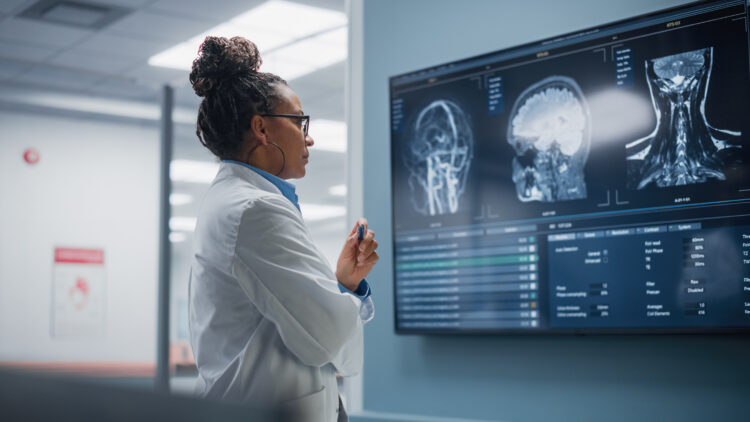
Diagnosis
A speech-language pathologist may perform a critical language examination using the signs and symptoms and the patient’s history, who, in this situation, has a brain injury or a stroke – to recognize aphasia. Other forms of brain imaging, such as MRIs and CT scans, may help identify the particular location and degree of damage to the brain that might trigger aphasia.
Recovery

Aphasia recovery is a long-term process that might last several years after the initial damage. Speech therapies should begin as soon as possible to obtain the best possible outcomes. However, for a variety of reasons, some patients have shown improvement rapidly and regained the ability to speak without any medical treatment.
Impact on Daily Life

One way aphasia can affect daily life is through the broad, extensive scope of its impact. As human beings communicate constantly, when communication is disrupted by aphasia, it negatively affects all aspects of one’s life. Social interactions can become stressful and uncomfortable, requiring individuals to deal with severe frustration as they try to engage in different lifestyle choices.
Research & Awareness

Brain scans and rehabilitation have significantly improved due to the development of modern science. Methods like fMRI and constraint-induced language therapy have helped identify the affected parts of the brain. Furthermore, promotion, awareness, and support by organizations, such as the National Aphasia Association and the Aphasia Recovery Connection, have ensured that many people understand aphasia and its effects.
It Does Not Affect Intelligence

There is a common misconception that people with Aphasia are less intelligent or have intellectual disorders. The belief that they are incapable of communicating effectively has nothing to do with their intellect. People with aphasia can think and ideate just like everyone else. The issue is that they have difficulty expressing these concepts and thoughts in words.
No Cure Or Treatment

There are currently no medications or medical procedures that can help treat aphasia. Following onset, long-term therapy, such as speech therapy and psychotherapy, is the only treatment available. Frequent therapy can assist the person in regaining control over their communication and verbal abilities, even if there is no 100% cure.

Comments
Loading…