
Autoimmune diseases are conditions where your immune system mistakenly attacks your own body, thinking it is fighting off harmful invaders. It can lead to a wide range of symptoms, some of which might not seem related at first. Here are 20 signs that you might have an autoimmune disease.
Fatigue

Fatigue may be a common signal of you having autoimmune diseases. This can happen when our immune system, by mistake, attacks our organs, resulting in swelling and irritation. Fatigues could make you feel tired all of the time, regardless of how much sleep or relaxation you are getting.
Joint pain

Joint pain in autoimmune diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis, takes place when your immune system attacks the liner of your joints. This causes swelling, mainly pain and stiffness within the joints. It is not only a little discomfort for now or then, but it can be a regular pain that could make it hard to move.
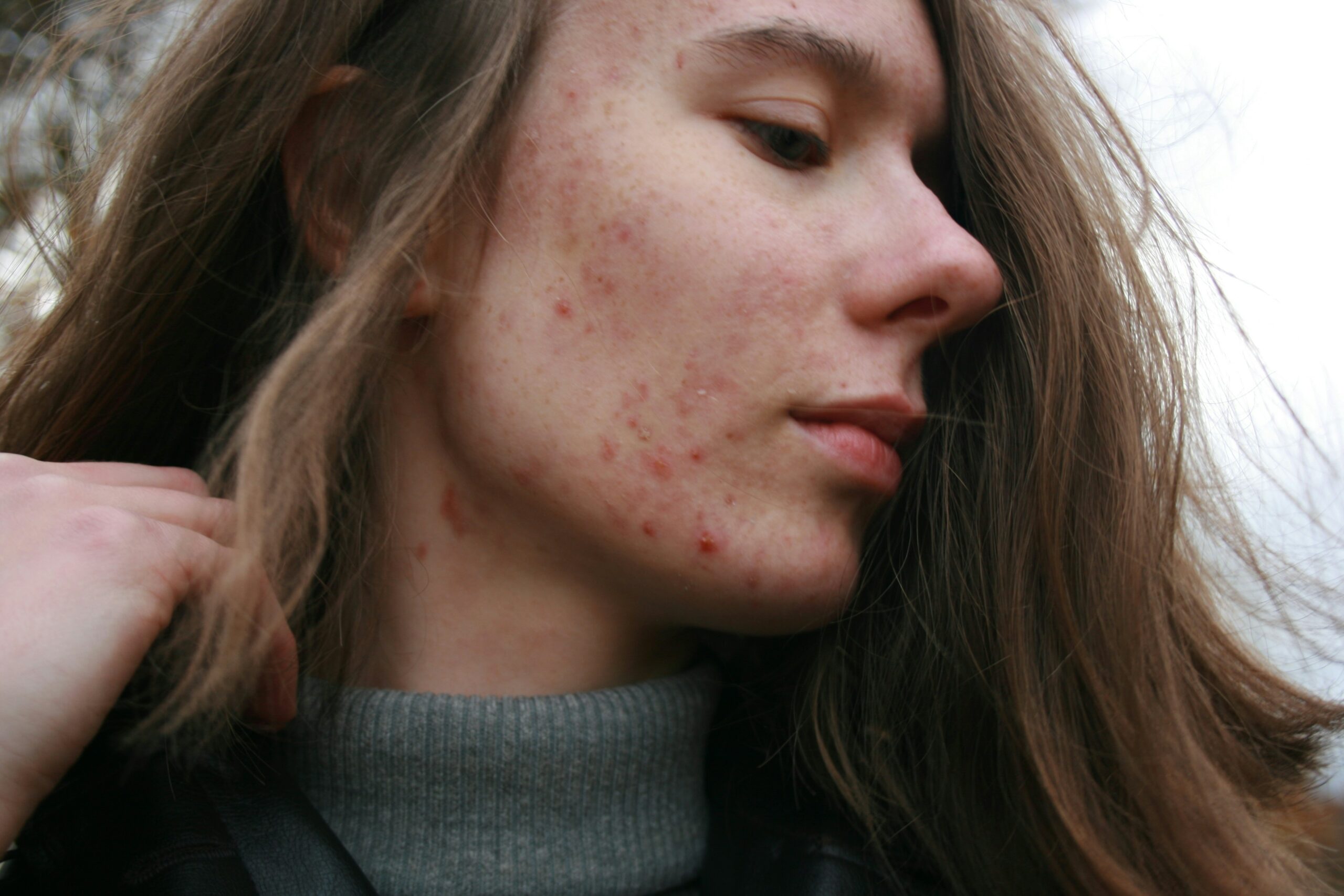
Skin issues

Skin troubles in conditions like psoriasis and lupus manifest when your immune device attacks your pores and skin cells. This can cause red, scaly patches, hives, or even blisters in your pores and skin. It is no longer only an ordinary rash or inflammation; it is your body’s response to your immune system attack, leading to inflammation.
Digestive problems

Digestive problems in diseases like Crohn’s disorder and ulcerative colitis occur when your immune system attacks the lining of your intestines. This can cause symptoms like stomach pain, diarrhea, or even bleeding. These signs may be repetitive and disrupt your daily life.
Weight changes

Weight changes, like unexpectedly losing or gaining weight without trying, can be a signal of an autoimmune disease. When your body is continuously inflamed, it may mess with your metabolism; that is how your body makes use of energy. This can cause your weight to go up or down all of a sudden.
Recurring fever

Recurring fever means having low-grade fevers that keep coming lower back with no clear cause. This can be a signal that your body is fighting against itself in an autoimmune response. When your body is in this sort of combat, it could make your body temperature go up.
Muscle aches

Muscle aches in autoimmune diseases are due to your immune system attacking your very own muscular tissues, leading to inflammation. This irritation causes pain and a feeling of weakness in your muscles. Unlike the brief pain you may experience after exercise, these muscle aches are deeper and more chronic.
Swollen glands
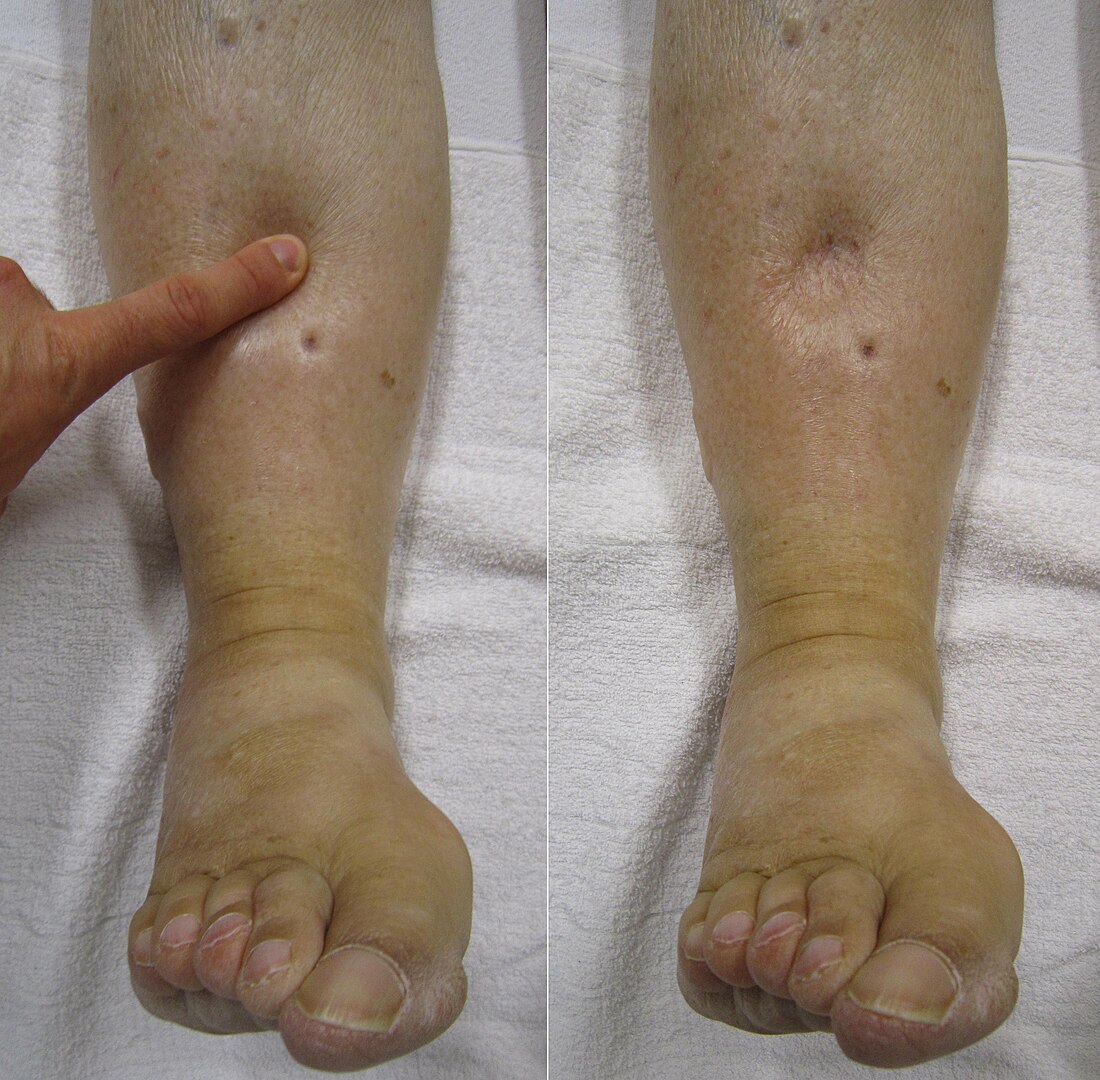
Enlarged lymph nodes mean that your immune system is working hard. In autoimmune diseases, this can occur because your body is attacking its very own tissues. This attack makes the glands in your lymph nodes swell up. It is like your body’s alarm system going off, showing that something is not right inside.
Hair loss

If you are experiencing thinning hair or bald patches, it can be a signal of autoimmune diseases like Graves’ sickness or Alopecia areata. Graves’ disease can cause brittle hair along with other symptoms like insomnia, irritability, weight loss, and shaky hands. Alopecia areata, however, specifically affects your hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss as your immune system mistakenly attacks these follicles, preventing hair growth.
Numbness or tingling

Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease that damages the protective covering around nerve cells within the brain and spinal cord, slowing down the transmission of messages in the primary nervous system. This damage can lead to signs like numbness, weakness, balance difficulties, and trouble walking.
Dry eyes or mouth

Sjögren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that affects the glands responsible for producing moisture in your eyes and mouth. As a result, people with this disease often experience dryness, infection, and soreness in these areas because of the reduced production of tears and saliva. This can cause complications like difficulty in swallowing and talking and also dental issues.
Cognitive difficulties

If you have an autoimmune disease, you may find it tough to be attentive and remember things. You could feel confused, forgetful, or like your mind is simply no longer as sharp as before. This might happen because you are not sleeping well, which is not unusual when your body is managing an infection.
Anemia

When you have an autoimmune disease, it can mess with how your body makes or keeps up with your red blood cells, leading to a condition called anemia. Red blood cells are important because they carry oxygen all over your body. If you do not have enough red blood cells, you might feel tired and weak, and your skin might look paler than usual.
Sensitivity to sun

Some autoimmune diseases make your skin more sensitive to sunlight, causing rashes or other bad reactions when you are out in direct sunlight. This happens because your immune system reacts strangely to the ultraviolet (UV) rays, thinking they are a threat and causing an inflammatory reaction in your skin.
Breathlessness

Autoimmune diseases like lupus can affect your lungs by causing inflammation. This inflammation is not caused by a lung infection but by your immune system attacking the tissue in your lungs by mistake. As a result, you might feel short of breath or have a constant cough.
Palpitations

Autoimmune diseases can sometimes affect your heart. When your immune system wrongly attacks your heart, it can cause inflammation. This inflammation can mess with the normal beating of your heart, leading to symptoms like irregular heartbeats or palpitations.
Mouth ulcers
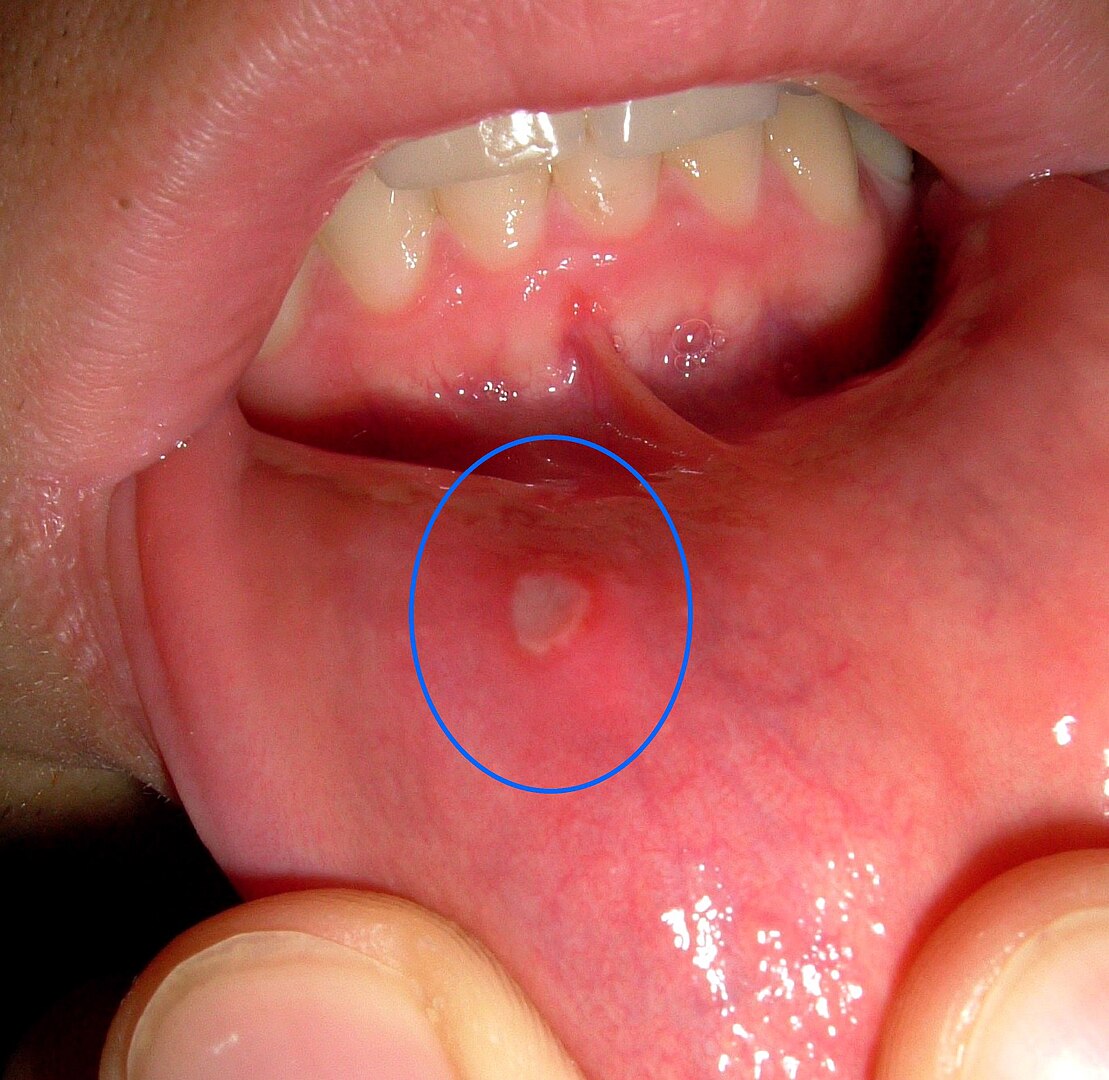
Having mouth ulcers that come back again and again might be a sign of certain autoimmune diseases, like Behçet’s disease or lupus. In Behçet’s disease, this immune response can cause painful ulcers in your mouth, as well as in other areas like your genitals and skin. If you keep getting mouth ulcers along with other symptoms, it is important to talk to a healthcare professional.
Chest pain

Chest pain is a serious symptom, and it’s important to take it seriously. In the context of autoimmune diseases, chest pain can sometimes be a sign of a condition like sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis is an autoimmune disease that causes tiny clumps of inflammatory cells called granulomas. When these granulomas form in your lungs or lymph nodes, they can cause chest pain.
Frequent headaches

Migraines are a form of headache that may be actually intense and might even make you feel unwell in your belly or sensitive to light and sound. If you notice that you are facing complications frequently or they feel different and more painful than before, it could be a sign to pay attention to.
Raynaud’s phenomenon

Raynaud’s phenomenon is a condition wherein your palms and feet can turn white or blue, and occasionally even red when you are exposed to cold temperatures or feeling stressed. This happens because the small blood vessels in your body narrow down, restricting blood flow to those areas.
Hair Loss
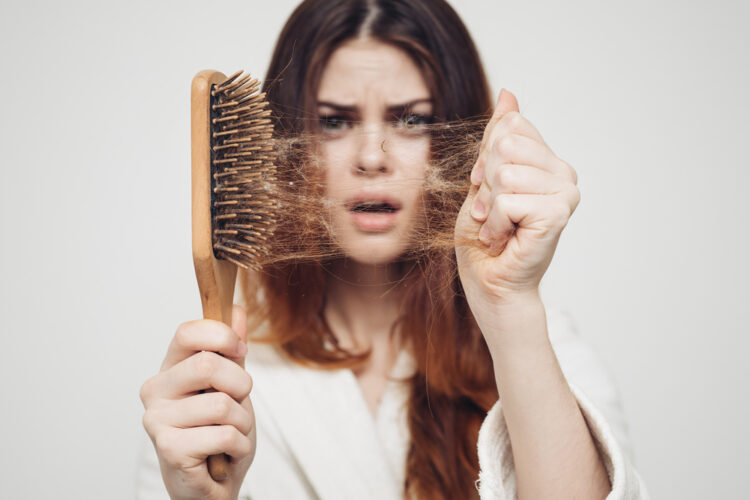

Hair loss can be a symptom of various autoimmune diseases, including alopecia areata, lupus, and thyroid disorders. In autoimmune-related hair loss, the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair thinning or bald patches. Treatment for hair loss associated with autoimmune diseases often involves managing the underlying autoimmune condition through medication and lifestyle changes, alongside specific therapies targeting hair regrowth.
Recurrent Infections

Recurrent infections can often trigger an overactive immune response, leading to the development of autoimmune diseases. The repetitive exposure to pathogens can dysregulate the immune system, causing it to mistakenly attack the body’s own tissues. This interplay between infections and autoimmunity underscores the complex relationship between immune function and disease susceptibility.
Insomnia or Disrupted Sleep Patterns

Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, can exacerbate symptoms of autoimmune diseases due to its impact on the body’s immune system regulation. Research suggests that insufficient sleep can trigger inflammation, potentially worsening the severity of autoimmune conditions. Managing insomnia effectively through lifestyle changes and therapy may help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with autoimmune diseases.
Depression and Mood Swings

Mood swings and depression are common symptoms experienced by individuals with autoimmune diseases, as the chronic pain and fatigue associated with these conditions can significantly affect mental health. The inflammation triggered by autoimmune responses can also have a direct impact on the brain, potentially altering neurotransmitter function and contributing to mood disturbances. Therefore, it is important for healthcare providers to address both the physical and psychological aspects of autoimmune diseases to ensure comprehensive patient care.
Thyroid dysfunction
Thyroid dysfunction, particularly conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, are common manifestations of autoimmune diseases where the immune system mistakenly attacks thyroid tissue. This can lead to an imbalance in thyroid hormones, causing symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, and mood disturbances. Proper management of thyroid function is crucial in patients with autoimmune conditions, as it can significantly improve quality of life and prevent further complications associated with thyroid hormone imbalances.
Nausea or vomiting

Nausea can be a nonspecific symptom associated with various autoimmune diseases, often as a result of inflammation or as a side effect of medication used to manage these conditions. For example, individuals with autoimmune disorders affecting the gastrointestinal tract, such as Crohn’s disease or autoimmune hepatitis, may experience nausea due to the direct impact of the disease on digestive functions. It is important for patients experiencing persistent nausea to consult with healthcare professionals, as it may indicate the need for a reassessment of their treatment plan or the presence of an underlying complication related to their autoimmune condition.
Dizziness or Fainting

Dizziness or fainting can sometimes signal underlying autoimmune conditions, such as multiple sclerosis or autoimmune inner ear disease, where the body’s immune response affects neurological or vestibular functions. These symptoms may also arise from autoimmune-related anemia, where a decrease in red blood cells leads to reduced oxygen delivery to the brain, causing episodes of lightheadedness or syncope. It is essential for individuals experiencing such symptoms to seek medical evaluation, as proper diagnosis and management of the underlying autoimmune disease can help mitigate these distressing and potentially dangerous episodes.
Nerve pain

Nerve pain, or neuropathic pain, can be a sign of certain autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or Sjögren’s syndrome, where the immune system’s attack on the body includes nerve tissue, leading to pain, tingling, or numbness. Conditions like Guillain-Barré syndrome, an acute autoimmune disorder, can cause severe nerve pain and weakness as the body’s immune response damages the peripheral nervous system. Proper diagnosis and treatment of the underlying autoimmune disease are crucial for managing nerve pain, which may involve the use of medications, physical therapy, and other interventions to reduce discomfort and improve nerve function.
Changes in Menstrual Cycle

Changes in the menstrual cycle, such as irregular periods or amenorrhea, can sometimes be indicative of underlying autoimmune diseases like thyroid disorders or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). These conditions can disrupt hormonal balance and ovarian function, leading to alterations in the menstrual cycle. It is important for individuals experiencing significant changes in their menstrual patterns to seek medical attention, as proper management of the autoimmune disease may help in restoring normal menstrual function and overall reproductive health.
Consult a Physician

It’s important to note that these symptoms can vary widely depending on the specific autoimmune disease and the individual’s unique circumstances. Additionally, experiencing one or more of these symptoms does not necessarily mean a person has an autoimmune disease, as they can also be indicative of other health conditions. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.

Comments
Loading…