Anesthesia is one of modern medicine’s greatest marvels, allowing for pain-free surgeries and procedures that would otherwise be unbearable. But what happens to your body when you’re under anesthesia? It’s more than just “falling asleep.” The process is full of surprises, from quirky bodily reactions to complex physiological changes. Let’s look into the intriguing world of anesthesia and uncover 15 fascinating ways your body reacts when you’re out cold.
Your Consciousness Fades Away
The first thing anesthesia does is put your mind to sleep. It works rapidly, usually within seconds, disconnecting your brain from your body’s sensations. This induced unconsciousness ensures you remain oblivious to the pain and sounds of surgery. Anesthesiologists monitor this carefully to keep you in just the correct depth of sleep.
Relaxation of Muscles
Muscle relaxation is essential for many surgical procedures. Anesthetics target the neuromuscular system, causing muscles to relax completely. The relaxation allows surgeons to operate more effectively. It also prevents involuntary movements that could complicate the surgery. After the procedure, muscle function gradually returns as the anesthesia wears off.
Altered Breathing Patterns
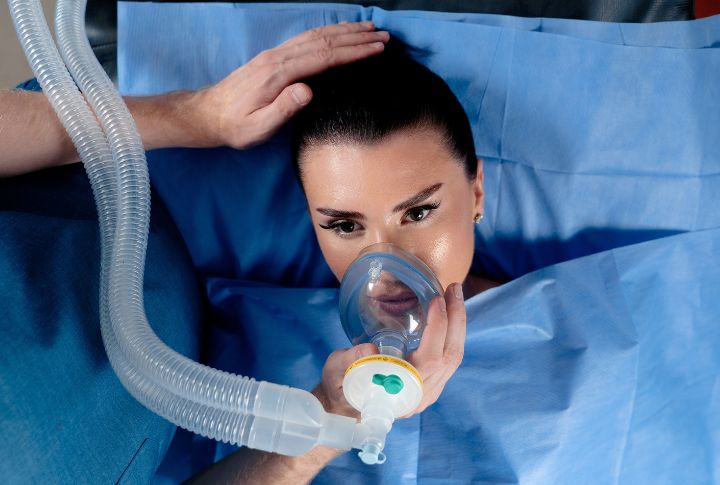
Breathing changes significantly under anesthesia. Most patients receive assistance from a ventilator to ensure adequate oxygen levels. Anesthetics can depress the respiratory system, making it less effective on its own. Medical teams carefully monitor oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Adjustments ensure that breathing remains stable and safe.
Changes in Hearing
Hearing can be temporarily affected. Some patients report muffled sounds or a ringing in the ears. These changes are due to the anesthetic drugs’ impact on the auditory system. Hearing returns to normal as the anesthesia wears off. It’s a transient effect that resolves without intervention.
Slowed Digestive Functions

Anesthesia slows down the digestive system, temporarily halting bowel movements. The reduced digestive effect helps prevent aspiration during surgery, where stomach contents could potentially enter the lungs. After the procedure, regular digestive activity can take some time to resume. Patients are advised to start with light foods as digestive functions resume.
Your Brain’s Communication Pathways Are Disrupted

Neural pathways that facilitate communication between different brain regions are interrupted. This disruption ensures you don’t feel pain or have any awareness of the surgery. As the anesthesia fades, these pathways gradually restore consciousness and normal brain function.
Enhanced Emotional Sensitivity

Some patients experience heightened emotional sensitivity after waking from anesthesia. This sensitivity can manifest as feelings of sadness, euphoria, or anxiety. The drugs’ effects on the brain, combined with the stress of surgery, can contribute to these emotional shifts. Medical professionals are trained to provide support and reassurance during this period. Emotional sensitivity usually diminishes as the patient fully recovers from the anesthesia.
Body Temperature Drops

A common effect of anesthesia is a drop in body temperature. Operating rooms are often kept cool, and anesthesia can reduce your body’s ability to regulate temperature. To counteract this, warming blankets or devices are used to keep you comfortable. Keeping your body at the right temperature helps prevent complications like hypothermia.
Nausea and Vomiting Can Occur

Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) are common side effects of anesthesia. Various factors, including the type of surgery and anesthetics used, can influence this. Anesthesiologists often administer anti-nausea medications to mitigate these effects. Despite preventive measures, some patients may still experience these symptoms. Understanding this potential side effect helps manage and alleviate discomfort post-surgery.
Your Body’s Stress Response Is Diminished

One of the benefits of anesthesia is its ability to dull the body’s stress response. Typically, stressful situations trigger the release of hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, but anesthesia can mitigate this reaction. This reduction helps maintain a stable heart rate and blood pressure during surgery.
Memory Blackout

Anesthesia often results in temporary amnesia, wiping out any recollection of the procedure. This memory blackout can extend from a few minutes after the anesthesia is administered to several hours afterward. The drug’s effect on the brain’s memory centers ensures you won’t remember any discomfort or pain. Interestingly, some patients report minor memory lapses even days after the surgery.
Reduced Blood Pressure

Many anesthetic agents cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to a drop in blood pressure. The anesthesiologist usually manages this effect by adjusting medication levels to keep blood pressure within a safe range. Low blood pressure helps reduce bleeding during surgery, which benefits the surgical team. Patients might feel dizzy or lightheaded upon waking as their bodies readjust.
Twitches and Shivers

Some patients experience muscle cramps or shivering as they emerge from anesthesia. These involuntary movements are typically harmless and result from the body’s effort to regain normal function. Shivering, in particular, is a typical response to the drop in body temperature during surgery. Warm blankets and gentle reassurance help patients through this phase.
Temporary Vision Changes

Emerging from anesthesia can sometimes result in blurred or double vision. The anesthetic drugs can temporarily affect the eye muscles and nerves, leading to these visual disturbances. Patients often find their vision stabilizes within a few hours as the drugs wear off. Until then, it is best to avoid straining the eyes, such as reading or using screens.
Cognitive Fog

Waking up from anesthesia often brings a sense of grogginess or confusion, commonly known as cognitive fog. This temporary mental cloudiness makes it challenging to focus or remember recent conversations. The brain’s response to anesthetic drugs causes this disorientation, which usually clears up within a few hours. Rest, hydration, and a calm environment can help speed up mental clarity.

Comments
Loading…