Numerous animal-borne illnesses affect Americans and thus require attention and safety measures. There are now more worries due to increased human-wildlife interactions. The chances of developing these infections and diseases increase as human settlements become more invasive in natural areas. Here are 20 animal-borne illnesses that should concern Americans.
Lyme Disease
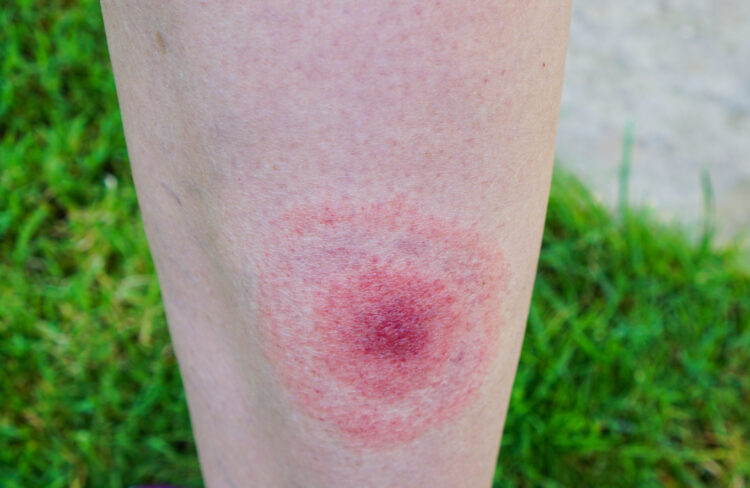
When you are out enjoying nature, especially in wooded or grassy areas, ticks can latch onto you and transmit the bacteria that causes Lyme disease. If you notice a rash like a bull eye or experience flu-like symptoms after a tick bite, you need to consult a doctor immediately, without any further delay.
West Nile Virus
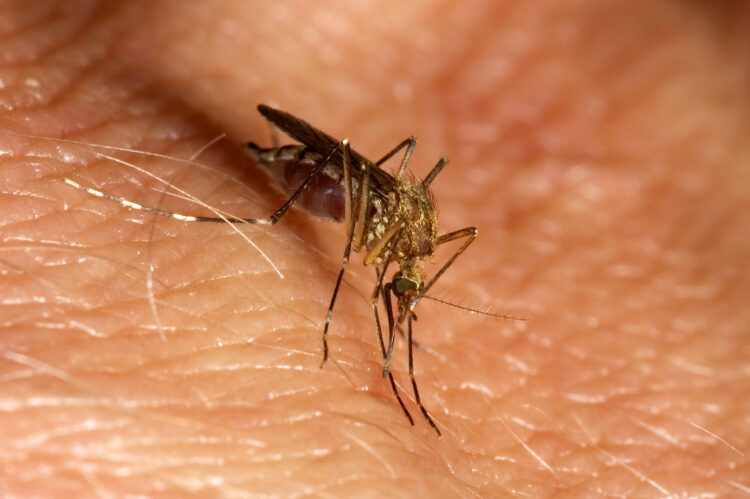
We all know how annoying mosquitoes are and the deadly diseases they can cause, such as dengue and Zika. Studies have shown that they can also carry the West Nile virus. This virus can cause severe headaches and skin rashes. If left untreated, it can cause deadly illnesses like encephalitis and meningitis.
Rabies

You might feel good hearing that rabies is not so prevalent in the United States. But in general, rabies can be a serious concern if you are bitten or scratched by rabid animals, like dogs, coyotes, bats, or raccoons. This viral disease affects the central nervous system, leading to brain disease and death if you leave it untreated.
Hantavirus
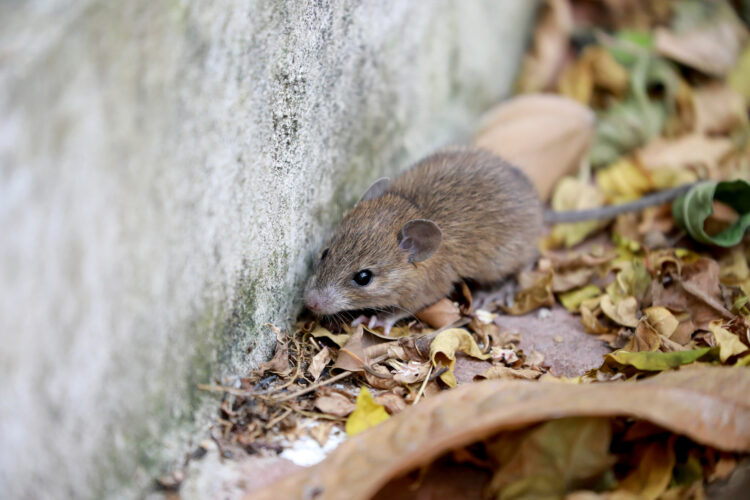

Hantavirus is majorly found in rodent droppings and urine. You are prone to getting infected by hantavirus if you inhale dust that contains rodent urine and feces. This can also happen when the infected dust gets into your eye or skin cuts while cleaning infested areas. Some common symptoms are muscle aches, fever, and sometimes abdominal pain.
Salmonella
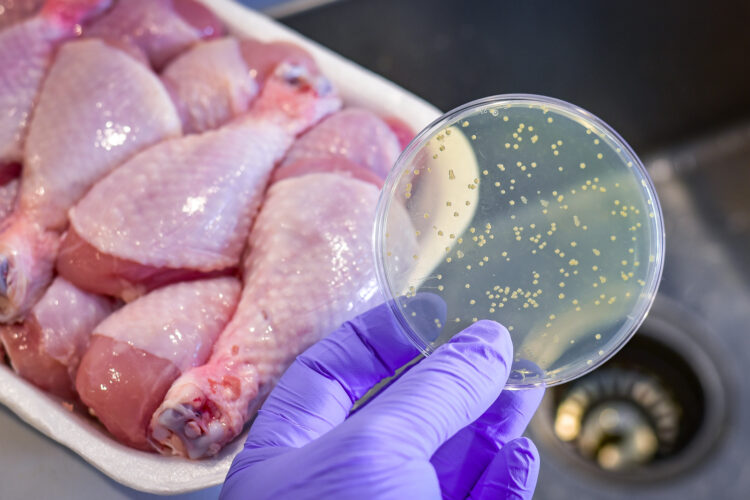
Salmonella is a type of bacteria mainly found in the intestinal tracts of reptiles, birds, and mammals. You are most likely to be infected by salmonella if you consume food or water that is contaminated with their feces. Avoid eating raw meat and eggs, and wash your fruits and vegetables as it lowers the risk of contamination.
Psittacosis
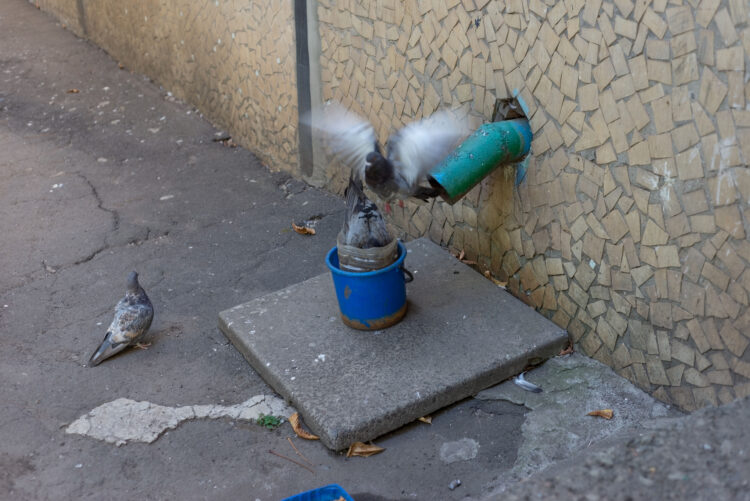

You will be shocked to know that common bird pets like parrots, parakeets, and other birds can carry this bacterial infection. Breathing dust contaminated with infected bird feces can cause this infection. If you experience symptoms like fever, cough, and difficulty breathing after exposure to birds, see your doctor for consultation.
Pasteurellosis
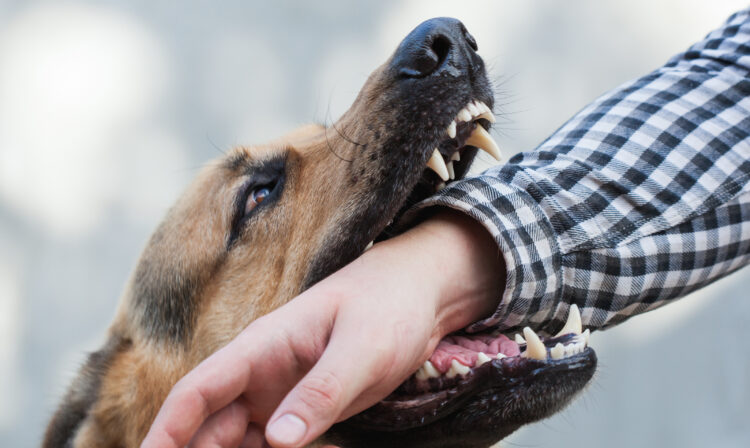

Pasteurella infections can be spread in several ways. You can breathe in tiny droplets in the air, have direct nose-to-nose contact, or eat or drink food and water contaminated by the nose and mouth discharges of infected animals. You can also get this infection from dog or cat bites.
Cat Scratch Disease
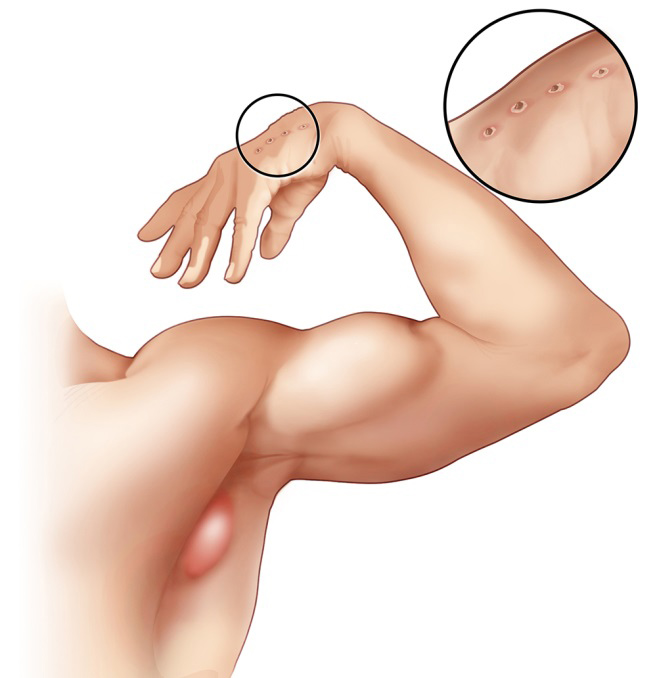
Cat Scratch disease is an infection caused by bacteria that spreads from cats. You can get this disease if an infected cat licks an open cut on your skin or if the cat bites or scratches you hard enough to make your skin bleed. You might experience symptoms like body rashes, fever, decreased appetite, and more.
Toxoplasmosis

If you are a cat owner, you should be aware of toxoplasmosis. It is a parasitic infection found in cat feces. The most common way people get this disease is by eating raw or uncooked meat. Pregnant women and people with weak immunity are more prone to this disease. Some symptoms are muscle pain and enlarged glands.
Newcastle Disease

The disease spreads when you come in direct contact with the bodily fluids of infected birds, particularly their feces. Even if you do not directly touch an infected bird, you could still be at risk if you touch objects or surfaces contaminated with their feces. Some symptoms are conjunctivitis, diarrhea, and coughing.
Ehrlichiosis
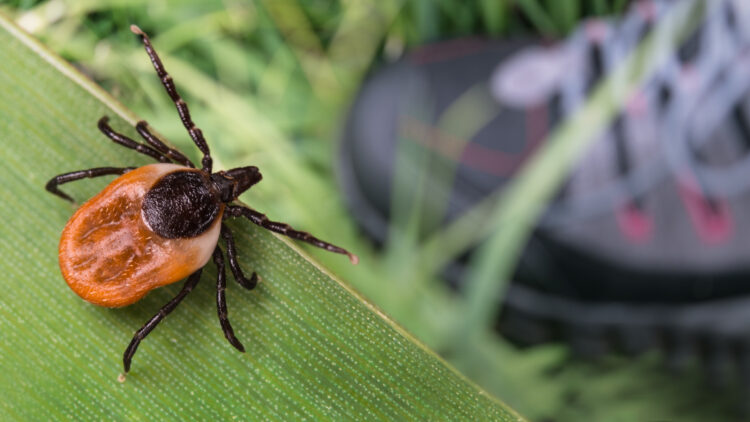

Ehrlichiosis is a bacterial infection spread by ticks. It commonly affects the white blood cells and can lead to fever, headache, lethargy, and muscle aches. If left untreated, the symptoms can worsen. Try prevention through insect repellents and protective gear. Although the condition improves, recovery depends on early detection and treatment.
Q-Fever

Q-Fever is defined by flu-like symptoms like fever, headaches, sore muscles, and lethargy. It is a bacterial infection that typically infects animals before spreading to people. Severe side effects like hepatitis or pneumonia can arise from it. Prevention primarily involves maintaining proper hygiene and avoiding contact with infected animals.
Tularemia

Tularemia is a bacterial infection that spreads by bug bites or contact with infected animals. As it infects humans, it displays symptoms like headache, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and skin ulcers. Although Tularemia is controllable through antibiotics, the best defense is to avoid wild animal contact. Also, dress cautiously when in locations where the disease is common.
Brucellosis
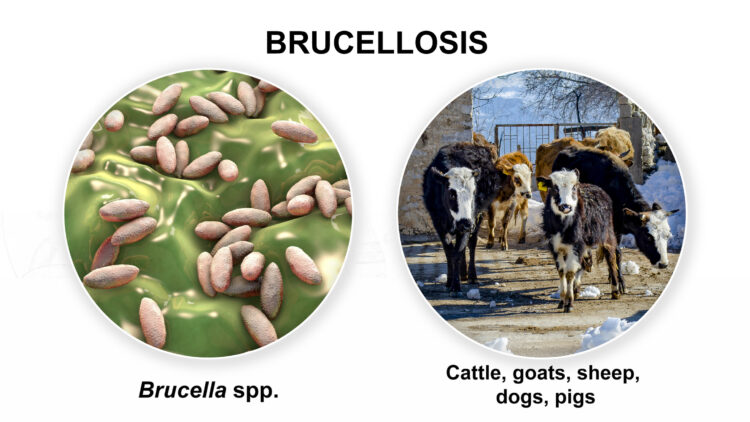
A bacterial infection, brucellosis is usually spread from animals to people. It is usually spread by eating contaminated animal products or by direct contact with infected animals. Fever, tiredness, joint discomfort, and muscular aches are some of its symptoms. Prevention includes maintaining proper hygiene and staying away from unpasteurized dairy products.
Chagas Disease
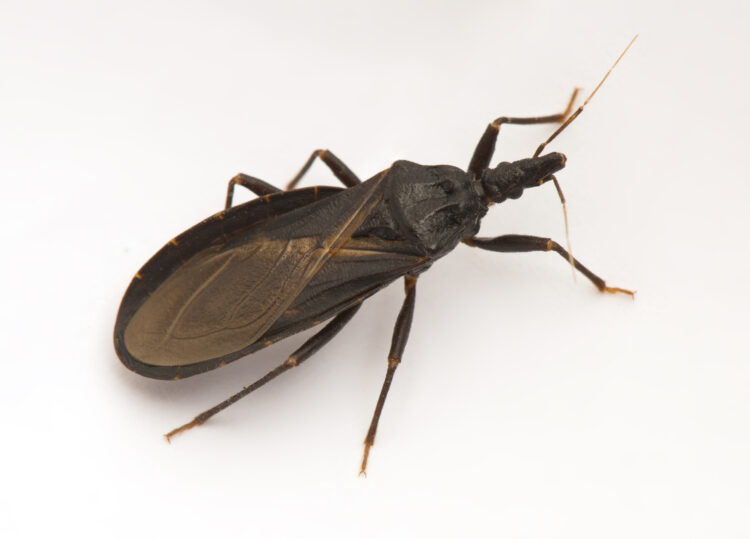

Chagas Disease is a parasitic infection spread by triatomine bugs. If infected, it will cause symptoms like exhaustion, high fever, body pain, and swelling. A persistent illness can lead to severe heart and intestinal issues. Applying insecticides and screening blood donors are examples of preventive strategies.
Plague

Plague is a bacterial infection that typically spreads by handling infected animals or flea bites. It appears as fever, chills, weakness, and enlarged lymph nodes. Antibiotic therapy must begin as soon as possible to avoid serious complications. Keeping fleas under control and avoiding contact with wild rodents are some preventive strategies.
Rat-Bite Fever
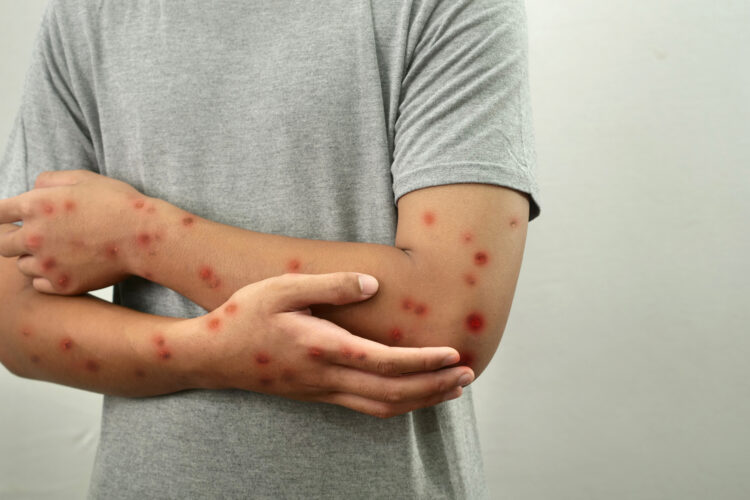
This bacterial infection develops by eating or drinking water contaminated with rodent waste. It also spreads by getting bitten or scratched by an infected rodent. Fever, rash, headaches, and sore muscles are among the symptoms. Prevention includes controlling rats and avoiding interaction with wild rodents.
Colorado Tick Fever
This viral infection spreads through the bite of a Rocky Mountain wood tick carrying the infection. It can lead to symptoms such as fever, headache, sore muscles, and fatigue. Although there is no specific treatment, supportive care can reduce symptoms. Preventive measures like insect repellents and avoiding tick habitats are helpful.
Monkeypox
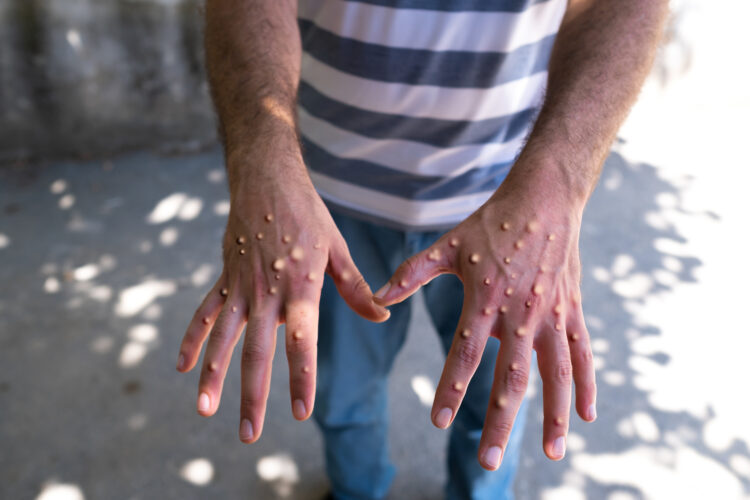

Monkeypox is a viral infection with similar symptoms to smallpox. It is primarily common in Central and West Africa. Monkeypox typically transmits to humans from rodents and primates. Some of its common symptoms include fever, rash, and enlarged lymph nodes. To prevent the same, avoiding contact with infectious animals and maintaining proper hygiene are important.
Avian Influenza
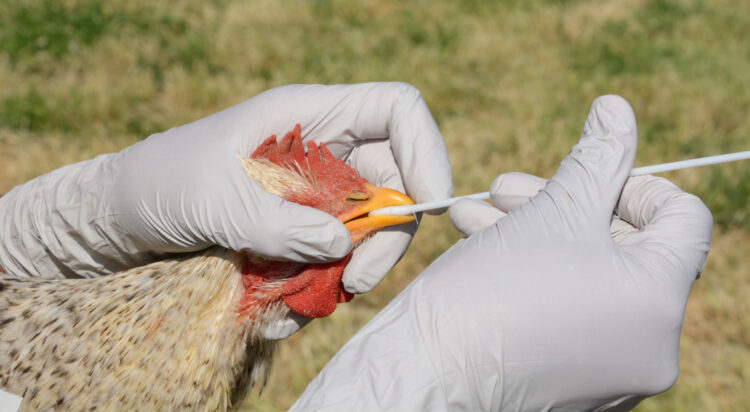
Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, is a virus that mainly impacts birds but can also occasionally infect humans. It can cause symptoms that range from a mild flu-like sickness to serious respiratory problems. Avoiding contact with sick birds and properly cooking (and cleaning) poultry products may help stop the spread of disease.

Comments
Loading…